信息隐藏是该实验主要要探究的内容。
实验目的 本次实验目的为运用信息隐藏技术,开发 hide 和 show 算法,能将一段超过1000个字符的内容通过 hide 算法隐藏在24位的 BMP 图片中,并且可以通过 show 算法将这段信息提取出来。
程序要能在其他文本文件和24位BMP图片上执行隐藏和恢复操作。
实验原理 该信息隐藏技术利用图像最低有效位(LSB)替换的原理,具体如下:
位平面分解 :将24位BMP图像的每个像素点的RGB分量(各8位)分解为8个位平面,从最高位(MSB)到最低位(LSB)。LSB替换 :选择最低位平面(对视觉影响最小)来隐藏信息,因为修改最低位对人眼几乎不可察觉。嵌入算法 :
对于待隐藏信息的每一位(0或1):
如果是0:将像素值的最低位置0 (AND 11111110)
如果是1:将像素值的最低位置1 (OR 00000001)
提取算法 :
读取每个像素值的最低位(AND 00000001)即可恢复隐藏的信息
实验过程 1.算法实现 hide 算法实现(旧) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 from PIL import Imagedef hide_text_in_image ():input ("请输入要隐藏的文本文件路径: " ).strip('"' )input ("请输入BMP图片路径: " ).strip('"' )input ("请输入保存后的图片路径: " ).strip('"' )try :with open (text_file, 'rb' ) as f:except FileNotFoundError:print (f"错误:找不到文本文件 {text_file} !" )return except Exception as e:print (f"读取文本文件时出错: {e} " )return try :open (image_file)if img.mode != 'RGB' :'RGB' )except FileNotFoundError:print (f"错误:找不到图片文件 {image_file} !" )return except Exception as e:print (f"读取图片时出错: {e} " )return len (text_data) * 8 if width * height < required_pixels:print (f"错误:图片太小!需要至少 {required_pixels} 像素,但图片只有 {width * height} 像素。" )return '' .join(format (byte, '08b' ) for byte in text_data)0 for y in range (height):for x in range (width):if index >= len (binary_str):break if index < len (binary_str):0xFE ) | int (binary_str[index])1 if index < len (binary_str):0xFE ) | int (binary_str[index])1 if index < len (binary_str):0xFE ) | int (binary_str[index])1 try :print (f"✅ 隐藏成功!图片已保存到: {output_image_file} " )except Exception as e:print (f"保存图片时出错: {e} " )if __name__ == "__main__" :print ("=== BMP图片隐写工具===" )input ("按 Enter 键退出..." )
show 算法实现(旧) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 from PIL import Imagedef show ():"""从BMP图片中提取隐藏的文本""" input ("请输入包含隐藏文本的BMP图片路径(如:C:\\隐藏的图片.bmp): " ).strip('"' )input ("请输入提取后的文本保存路径(如:C:\\提取结果.txt): " ).strip('"' )try :open (image_file)if img.mode != 'RGB' :'RGB' ) except Exception as e:print (f"❌ 读取图片失败: {e} " )return for y in range (height):for x in range (width):str (r & 1 )) str (g & 1 )) str (b & 1 )) for i in range (0 , len (binary_data), 8 ):8 ]if len (byte_bits) < 8 :break int ('' .join(byte_bits), 2 )try :with open (output_text_file, 'wb' ) as f:bytes (text_bytes))print (f"✅ 文本提取成功!已保存到: {output_text_file} " )except Exception as e:print (f"❌ 保存提取结果失败: {e} " )if __name__ == "__main__" :print ("=== BMP隐藏文本提取工具 ===" )input ("按 Enter 键退出..." )
问题与反思 经过实验后,这两段代码都能准确的将文本隐藏进去和提取出来,但是出现了一个新的问题,就是在提取出来的文本中,除了原本存放进去的文本,后面还跟着一大串的二进制数据。这样的结果不是我想要的,于是开始思考有什么方法可以解决。
思考过后,我想出的方法为添加文件头并且确定文本字符长度,让 show 算法可以准确提取相应的文本。
hide 算法实现(新) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 from PIL import Imagedef hide_text_in_image ():input ("请输入要隐藏的文本文件路径: " ).strip('"' )input ("请输入BMP图片路径: " ).strip('"' )input ("请输入保存后的图片路径: " ).strip('"' )try :with open (text_file, 'rb' ) as f:len (text_data).to_bytes(4 , byteorder='big' )except Exception as e:print (f"❌ 读取文本失败: {e} " )return '' .join(format (byte, '08b' ) for byte in text_data_with_length)try :open (image_file)if img.mode != 'RGB' :'RGB' )except Exception as e:print (f"❌ 读取图片失败: {e} " )return len (text_data_with_length) * 8 if width * height < required_pixels:print (f"❌ 图片太小!需要 {required_pixels} 像素,实际 {width * height} 像素" )return 0 for y in range (height):for x in range (width):if index >= len (binary_str):break if index < len (binary_str):0xFE ) | int (binary_str[index])1 if index < len (binary_str):0xFE ) | int (binary_str[index])1 if index < len (binary_str):0xFE ) | int (binary_str[index])1 try :print (f"✅ 隐藏成功!图片已保存到: {output_image_file} " )except Exception as e:print (f"❌ 保存图片失败: {e} " )if __name__ == "__main__" :print ("=== BMP图片隐写工具 ===" )input ("按 Enter 键退出..." )
show 算法实现(新) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 from PIL import Imageimport tracebackdef show ():"""从BMP图片中提取隐藏的文本""" try :input ("请输入BMP图片路径: " ).strip('"' )input ("请输入输出文本路径: " ).strip('"' )open (image_file)if img.mode != 'RGB' :'RGB' )0 for y in range (height):for x in range (width):if bits_collected >= 32 :break if bits_collected < 32 :str (r & 1 ))1 if bits_collected < 32 :str (g & 1 ))1 if bits_collected < 32 :str (b & 1 ))1 int ('' .join(length_bits), 2 )print (f"[调试] 隐藏文本长度: {text_length} 字节" )bytearray ()8 0 for y in range (height):for x in range (width):if bits_collected >= bits_needed:break if bits_collected < bits_needed:str (r & 1 ))1 if bits_collected < bits_needed:str (g & 1 ))1 if bits_collected < bits_needed:str (b & 1 ))1 while len (byte_buffer) >= 8 :int ('' .join(byte_buffer[:8 ]), 2 )8 :]with open (output_text_file, 'wb' ) as f:4 :4 + text_length]) print (f"✅ 提取完成!结果已保存到: {output_text_file} " )except Exception as e:print (f"❌ 错误:\n{traceback.format_exc()} " )if __name__ == "__main__" :print ("=== BMP隐藏文本提取工具 ===" )input ("按 Enter 键退出..." )
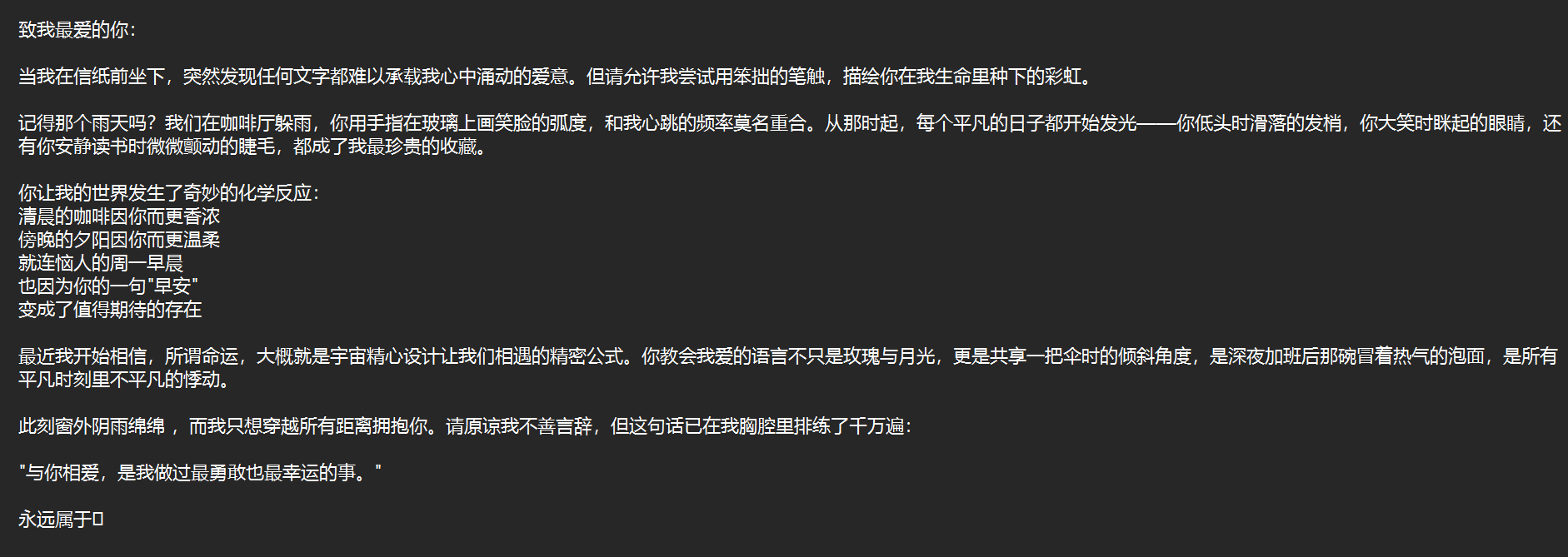
2.运行结果展示 原文本
原图片
hide 函数运行结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 PS D:\cprogram> & C:/Users/13483/AppData/Local/Microsoft/WindowsApps/python3.11.exe d:/cprogram/two/view_hide.py"C:\Users\13483\Desktop\纪念\致我最爱的你.txt" "C:\Users\13483\OneDrive\图片\QQ20250416-103939.bmp" "C:\Users\13483\OneDrive\图片\QQ20250416-103939(1).bmp"
隐藏后图片展示
show 函数运行结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 PS D:\cprogram> & C:/Users/13483/AppData/Local/Microsoft/WindowsApps/python3.11.exe d:/cprogram/two/view_show.py"C:\Users\13483\OneDrive\图片\QQ20250416-103939(1).bmp"
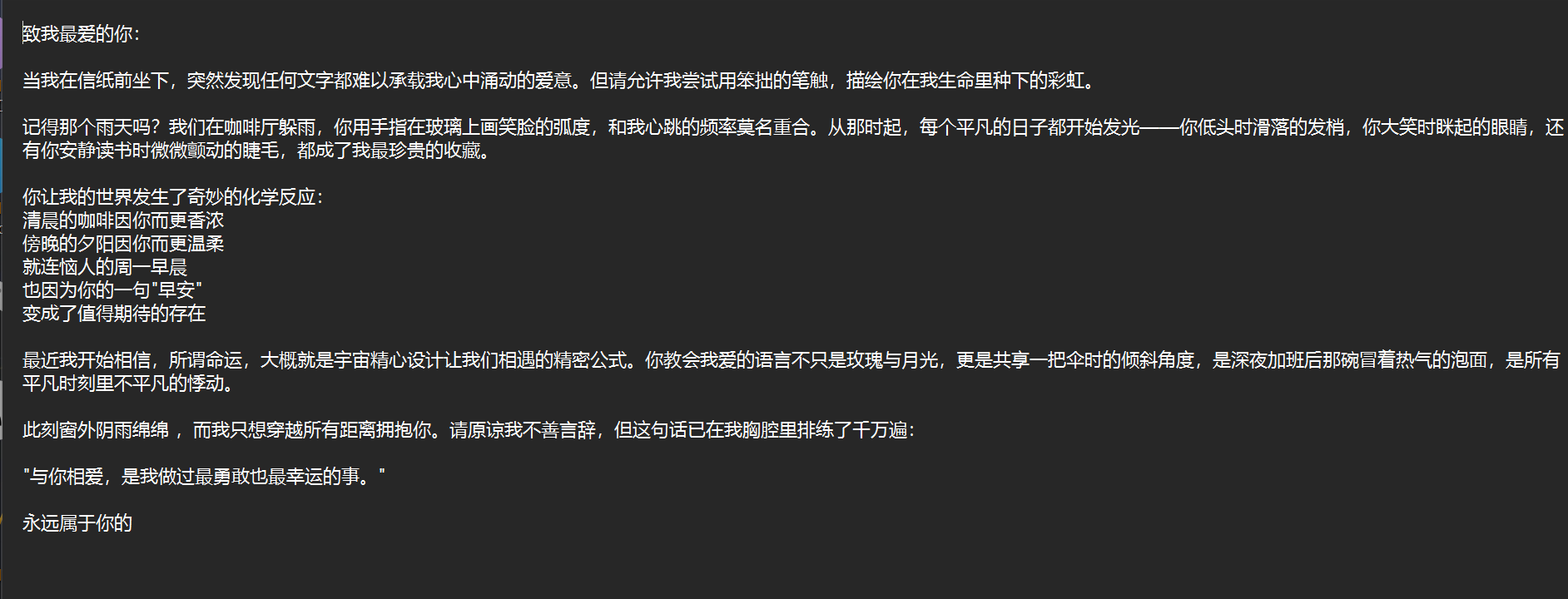
提取文本展示
可以看到,实验很成功。
思考和总结 如何储藏隐藏的内容长度 1. 长度头设计原理 在隐藏数据前,先在文件头部预留固定4字节空间,以大端序(big-endian)存储原始文本的字节长度值。这种设计具有:
固定开销 :仅增加4字节(32bit)的存储成本超大容量 :最大可表示4GB内容(2^32-1字节)快速解析 :提取时优先读取这4字节即可获知数据量
2. 具体实现方法 隐藏阶段(hide): 1 2 3 len (text_data).to_bytes(4 , byteorder='big' )
提取阶段(show): 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 0 for y in range (height):for x in range (width):if bits_collected >= 32 :break if bits_collected < 32 :str (r & 1 ))1 if bits_collected < 32 :str (g & 1 ))1 if bits_collected < 32 :str (b & 1 ))1 int ('' .join(length_bits), 2 )
3. 技术优势
精准控制 :完全避免读取多余像素数据格式兼容 :与任何文件类型(txt/jpg/exe等)兼容抗干扰性 :长度头损坏会立即发现,避免错误解析
关键问题与解决
数据污染 :通过添加4字节长度头标记,精确控制提取范围字节对齐 :严格按比特数控制提取,实时转换字节流格式限制 :选用24位BMP保证数据完整性
改进方向
安全性 :增加AES加密容错性 :添加纠错编码易用性 :开发GUI界面
核心收获
掌握LSB隐写基本原理
提升二进制数据处理能力
理解信息隐藏的不可感知性特性
实验验证了LSB技术的可行性,后续可结合加密算法构建更安全的隐写系统。

.bmp)